

The canal for the saccular branch of the inferior vestibular nerve was located just below the canal for the superior vestibular nerve, and that for the posterior ampullary nerve, the so-called singular canal, ran laterally or posteolaterally from the posteroinferior aspect of the canal for the saccular branch.ĬONCLUSION: Five bony nerve canals in the fundus of the internal auditory canal were detected by high-frequency on high-resolution temporal bone CT. The canal for the cochlear nerve was located just below that for the labyrinthine segment of the facial nerve, while that canal for the superior vestibular nerve was seen at the posterior aspect of these two canals. In all detectable cases, the canal for the labyrinthine segment of the facial nerve was revealed as one which traversed anterolaterally, from the anterosuperior portion of the fundus of the internal auditory canal. On coronal CT images, canals for the labyrinthine segment of the facial and superior vestibular nerve were seen in 100% of cases, but those for the cochlear nerve, the saccular branch of the inferior vestibular nerve, and the singular canal were seen in 90.1%, 87.4% and 78% of cases, respectively. Four canals were identified on axial CT images in 100% of cases the so-called singular canal was identified in only 68%. RESULTS: Five bony canals in the fundus of the internal auditory canal were identified as nerve canals. Three radiologists determined the detectability and location of canals for the labyrinthine segment of the facial, superior vestibular and cochlear nerve, and the saccular branch and posterior ampullary nerve of the inferior vestibular nerve. Those with a history of uncomplicated inflammatory disease were included, but those with symptoms of vertigo, sensorineural hearing loss, or facial nerve palsy were excluded.
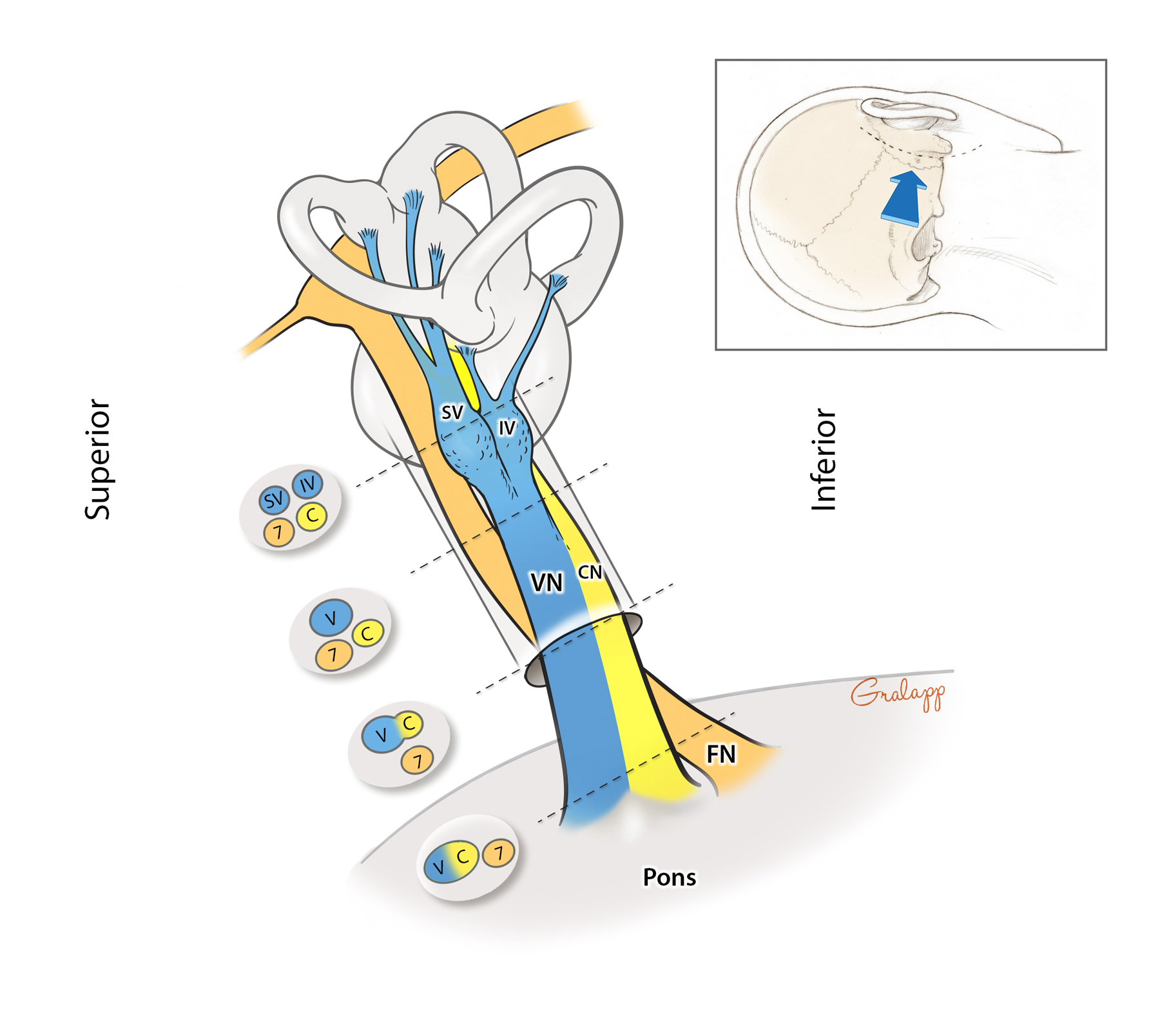

MATERIALS AND METHODS: We retrospectively reviewed high-resolution (1 mm thickness and interval contiguous scan) temporal bone CT images of 253 ears in 150 patients who had not suffered trauma or undergone surgery. Containing over 700 vibrant, full-colour images, TeachMeAnatomy is a comprehensive anatomy encyclopedia presented in a visually-appealing, easy-to-read. PURPOSE: To identify and evaluate the normal anatomy of nerve canals in the fundus of the internal auditory canal which can be visualized on high-resolution temporal bone CT.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
